How Does a Peltier Cooler Work: Peltier Effect
A Peltier cooler is a compact and precise cooling solution used in electronics, laboratory instruments, and semiconductor tools. Many engineers know it relies on the Peltier effect, but few understand what actually happens inside the thermoelectric module.
This article explains how a Peltier device moves heat using only electricity.
What Is a Peltier Cooler?
A Peltier cooler is a thermoelectric cooling device that creates a cold side and a hot side when electricity flows through a Peltier module. It offers solid state cooling without refrigerants and is commonly used in applications that require stable and vibration free temperature control.
A typical Peltier cooler, also called a thermoelectric cooler or TEC, uses one or more thermoelectric modules to absorb heat from a target and move it to a heat sink or liquid loop. The system is small, quiet, and easy to integrate because it contains no compressor, valves, or moving parts besides a fan or pump.
Engineers use Peltier coolers in laser stabilization, sensor cooling, benchtop analyzers, and compact devices where precise thermoelectric cooling is important.
What Is the Peltier Effect?
The Peltier effect is a thermoelectric phenomenon. The core of Peltier cooling is that when an electric current passes through semiconductors of different materials, electrons at the junction absorb or release heat. This effect allows a solid state device to cool without refrigerant or mechanical compression.
Why Can a Peltier Module Produce Cooling?
The “cooling” produced by a Peltier cooler is simply the result of heat being removed from the cold surface. A Peltier module can cool because the electrons inside its semiconductor pillars change their energy state as current passes through them.
Each module contains many N-type and P-type semiconductor legs. When electrons move from one type of semiconductor to the other, they must absorb energy to reach a higher energy level.
They draw this energy directly from the cold side of the module, and in real applications that energy comes from the object being cooled. As the module absorbs this heat, the temperature of the object drops.
This is not mechanical cooling, but cooling created by the microscopic behavior of electrons inside thermoelectric materials.
Peltier chiller transfers heat from the cold side to the hot side using electrical power.
Why Does a Peltier Cooler Need Heat Dissipation?
All the heat absorbed from the cold side is pushed to the hot side, and the module also generates extra heat internally because of electrical resistance.
For example, cooling a 20 watt laser diode might require the hot side to reject 30 to 40 watts of heat once electrical input is included.
If this heat is not removed quickly through a heat sink or a liquid cooling system, the temperature on the hot side will rise. Once that surface becomes too warm, the temperature difference between the two sides will collapse and the cold side will no longer stay cold.
This is why every Peltier cooler, including small TEC modules and larger Peltier chillers, relies on effective heat dissipation. The cooler can only keep working when the hot side stays cool enough and the cold side remains significantly lower in temperature.
How Does a Peltier Cooler Work?
A Peltier cooler applies the Peltier effect in a complete system to move heat from a target object to the environment. One or more thermoelectric modules are placed between a cold plate and a heat sink.
The cold plate draws heat from the object or fluid, and the modules transfer it to the hot side. The hot side releases heat through a fan, heat sink, or liquid cooling loop.
A temperature controller adjusts the current to maintain the desired temperature. Increasing current strengthens cooling, while decreasing it reduces cooling. This setup allows Peltier chillers to precisely control temperatures in sensitive equipment such as CCD or CMOS sensors, laser modules, analytical instruments, and small fluid circulation systems.
Some Peltier coolers can even reverse the current, turning the device into a heating system if needed.
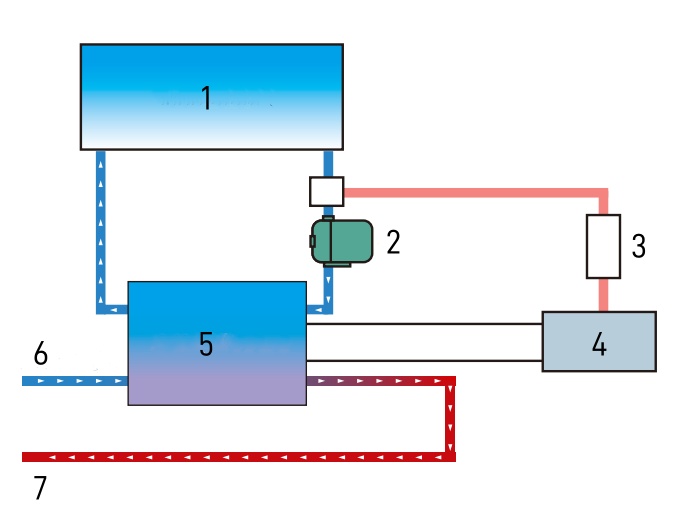
1.Chuck wafer carrier
2.Circulation pump
3.Controller
4.Thermoelectric heat exchange module
5.Power module
6.Cooling water inlet
7.Cooling water outlet
What Affects the a Peltier Cooler Cooling Capacity?
The cooling capacity of a Peltier cooler depends on the module size, the amount of current applied, the temperature difference required, and how efficiently the hot side releases heat. These factors determine how much real cooling the system can deliver.
1.Module Size and Number of TECs
Larger thermoelectric modules or systems with multiple Peltier elements can move more heat, resulting in higher cooling capacity. However, bigger modules also generate more internal heat and require more efficient heat dissipation to maintain performance.
2.Electrical Current and Voltage
The cooling effect increases as more current flows through the Peltier module. Initially, higher current strengthens the heat transfer from the cold side to the hot side. Beyond a certain point, additional current produces excessive internal heat, reducing efficiency and limiting the net cooling capacity.
3.Temperature Difference (ΔT) Between Cold and Hot Sides
The greater the temperature difference required between the cold side and the hot side, the harder the module has to work. Peltier modules have a maximum ΔT rating. As the temperature difference approaches this limit, the remaining cooling power diminishes, making it difficult to maintain very low temperatures.
4.Heat Dissipation on the Hot Side
If the heat sink or liquid cooling system cannot carry away heat quickly enough, the hot side temperature rises. This reduces the temperature difference across the module, lowering the cooling capacity of the cold side.
5.Thermal Interface Quality
The materials and contact quality between the Peltier module, cold plate, and heat sink significantly affect performance. Poor thermal contact or low-conductivity materials create resistance, which reduces heat transfer efficiency and lowers the effective cooling power.
6.Ambient Temperature
High ambient temperature increases the load on the Peltier module because the hot side becomes harder to cool. Conversely, cooler ambient conditions allow more efficient heat rejection, improving the cold side temperature and overall cooling performance.
Get a more efficient and reliable cooling solution.
Peltier Coolers from LNEYA
With over 15 years of experience in industrial temperature control, LNEYA provides tailored TEC based cooling solutions to match different application needs.
 LNEYA Industrial Chillers Manufacturer Supplier
LNEYA Industrial Chillers Manufacturer Supplier
















