What Are Water-Cooled Condensers

- Industrial Chiller vs Industrial Freezer
- What Are Water-Cooled Condensers
- Custom Chiller vs Standard Chiller
- Che cos'è un refrigeratore raffreddato ad aria
- Che cos'è un refrigeratore raffreddato ad acqua
- Refrigeranti a basso GWP nei refrigeratori per semiconduttori
- Che cos'è una camera di combustione
- Perché i test sui chip hanno bisogno di refrigeratori per semiconduttori
- Agosto 2025
- Luglio 2025
- Giugno 2025
- Maggio 2025
- Marzo 2025
- Febbraio 2025
- Gennaio 2025
- Dicembre 2024
- Novembre 2024
- Ottobre 2024
- Settembre 2024
- Agosto 2024
- Luglio 2024
- Giugno 2024
- Maggio 2024
- Aprile 2024
- Marzo 2024
- Febbraio 2024
- Settembre 2023
- Luglio 2023
- Giugno 2023
- Maggio 2023
- Gennaio 2023
refrigeratore raffreddato ad aria refrigeratore Installazione di un refrigeratore refrigeratori Congelatore a freddo refrigeratore di raffreddamento circolatore di raffreddamento e riscaldamento sistema di raffreddamento e riscaldamento cooling system Reattore in vetro a doppio strato sistema di controllo dinamico della temperatura congelatore refrigeratore a gas circolatore di riscaldamento refrigeratore industriale raffreddamento industriale congelatore industriale frigorifero industriale reattore a camicia refrigeratore a liquido refrigeratore a bassa temperatura notizie refrigeratore farmaceutico refrigeratore di processo reattore refrigeratore raffreddamento del reattore raffreddamento del reattore riscaldamento riscaldamento del reattore raffreddamento sistema di reattori circolatore refrigerato refrigeratore a refrigerazione refrigeratore a vite refrigeratore per semiconduttori refrigeratore di prova per semiconduttori sundi tcu controllo della temperatura camera di prova termostato refrigeratore a bassissima temperatura refrigeratore di prova per veicoli refrigeratore d'acqua refrigeratore raffreddato ad acqua wtd
Water-cooled condensers are a key component in many industrial cooling systems, especially in large-scale water-cooled chillers. Cooling systems use water as a cooling medium to remove heat from the refrigerant, condensing the vapor back into liquid. The water absorbs the heat and is then discharged, allowing the cycle to repeat.
These condensers are often preferred in situations where air-cooled systems wouldn’t be as efficient, particularly in environments where space is limited or where higher efficiency is needed.
How Do Water-Cooled Condensers Work?
Water-cooled condensers operate based on a simple yet effective heat exchange process. The refrigerant, which is in gaseous form after being compressed by the compressor, enters the condenser coils. Here, it meets the cooling water, which flows through the condenser’s cooling tubes or shell.
As the hot refrigerant passes through the condenser, it transfers its heat to the water. The water absorbs this heat and cools the refrigerant, causing it to condense back into a liquid state. The heated water is then pumped away and replaced by cooler water to repeat the process.
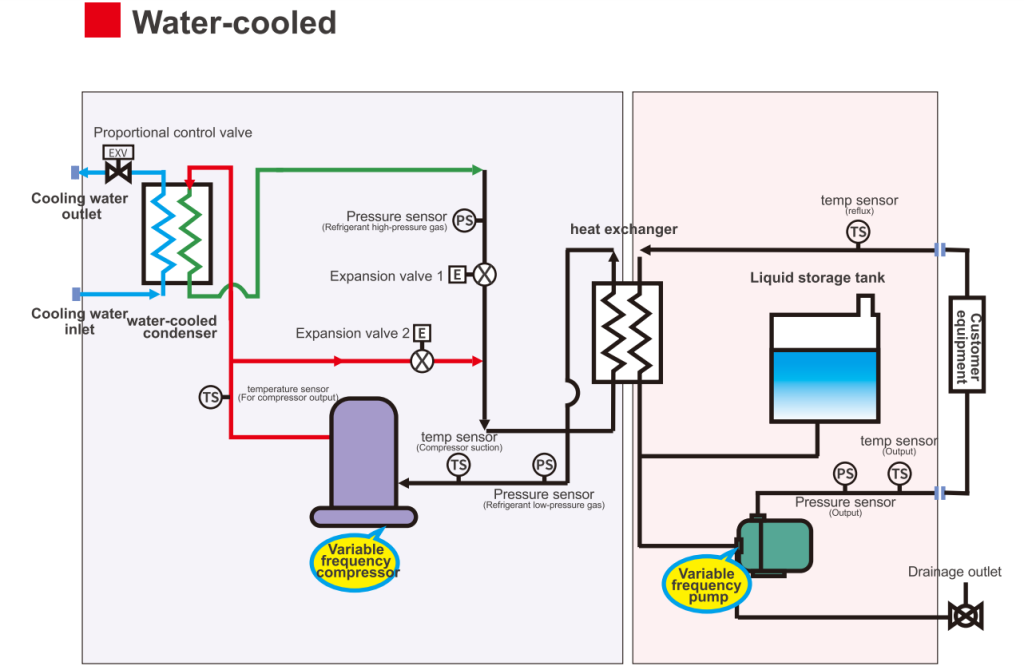
Types of Water-Cooled Condensers for Industrial Use
In industrial settings, several types of water-cooled condensers are commonly used. Each type is suited to different applications, depending on factors like size, cooling load, and space availability.
Shell and Tube Condensers
This is one of the most commonly used types in larger industrial systems. In this design, water flows through the tubes while the refrigerant flows over the tubes, allowing heat exchange to take place effectively.
Plate Heat Exchanger Condensers
In these systems, refrigerant flows through plates with cooling water passing in parallel channels. The plates create a highly efficient heat exchange surface, making this type ideal for situations where space is limited.
Air-Over-Water Condensers
This type combines both air and water cooling. A fan blows air across the water-cooled condenser coils, helping to enhance the cooling process. These are commonly used when there is a need for a combined approach in heat dissipation.
What Are the Advantages of a Water-Cooled Condenser?
Water-cooled condensers offer several advantages that make them particularly appealing in certain applications.
Higher Efficiency
Water is a more effective heat transfer medium compared to air. This makes water-cooled condensers more efficient, especially in high-load or continuous cooling applications.
Compact Design
These systems are often more compact than air-cooled alternatives, making them ideal for facilities where space is at a premium.
Consistent Cooling Performance
Water temperature is less susceptible to fluctuations than air temperature, which means water-cooled condensers can provide more stable and reliable cooling over time.
Lower Operating Costs
While the initial setup for a water-cooled system can be higher, the long-term operating costs are often lower. The enhanced efficiency means less energy is required to cool the refrigerant, which can significantly reduce energy bills.
When Does a Chiller Use a Water-Cooled Condenser?
Chillers with water-cooled condensers are used in environments that require efficient and consistent cooling, particularly when air-cooled systems would not perform as effectively. For example, large-scale industrial operations such as data centers, chemical processing plants, and manufacturing facilities often use water-cooled condensers to maintain a consistent temperature.
Water-cooled condensers are also ideal for systems that need to operate in high-heat environments or need to cool larger amounts of refrigerante efficiently.
What Is the Difference Between Air-Cooled Condensers and Water-Cooled Condensers?
While both types of condensers serve the same basic purpose — cooling the refrigerant and turning it from gas back into liquid — they operate differently and have distinct advantages.
Cooling Medium
Air-cooled condensers use air to remove heat, while water-cooled condensers use water. Water, being more effective at heat transfer, allows for higher efficiency and more reliable cooling.
Requisiti di spazio
Air-cooled condensers tend to take up more space because they rely on larger surface areas for heat exchange. Water-cooled condensers, on the other hand, are more compact and can fit into smaller spaces.
Consumo di energia
Water-cooled systems generally consume less energy than air-cooled systems because water transfers heat more efficiently. This means water-cooled systems can often provide the same level of cooling with lower energy usage.
Maintenance Needs
Air-cooled condensers are typically easier to maintain, as they don’t require a water supply system. Water-cooled condensers, however, need regular maintenance to ensure that the water system is clean, the water treatment is adequate, and there are no blockages in the pipes.
Talk to LNEYA Cooling Experts
Choosing the right cooling technology is a big decision. Whether a robust water-cooled condenser is the perfect heart for your sistema di refrigerazione, or another solution makes more sense, you don’t have to figure it out alone.
With years of experience across countless industries, our experts at LNEYA can cut through the complexity. We’ll help you understand the real-world pros and cons for your specific application, environment, and goals.
Stop guessing. Get a clear answer tailored to your plant’s needs. Reach out to our team today for a consultation.
Related Chillers
CONTATTO
TEL:TELEMATICO
EMAIL: EMAIL: EMAIL: EMAIL: EMAIL: EMAIL: EMAIL
WeChat e WhatsApp: il nostro servizio

Wechat QR

Hai domande o hai bisogno di un preventivo? Compila il modulo sottostante e il nostro team ti risponderà entro 24 ore.
 Refrigeratori industriali LNEYA Produttore Fornitore
Refrigeratori industriali LNEYA Produttore Fornitore



















